- February 10, 2026
- Categories: Web Solutions
A Complete Guide to HTTP 500 Server Error Codes
HTTP status codes are the signals between a website server and web browser. You never notice them if the website information loads normally. But when the server cannot complete the request, the browser may show an error page instead of the website.
An HTTP 500 Server Error is a server side error. It affects user experience and business performance. This happens because the page fails to load properly.
Did you know that 41% of the companies report their hourly downtime cost between $1 million and $5 million in 2025?
A 500 error means the server hit a problem and could not complete the request. First, reload the page and clear cache. This helps rule out local glitches. If it keeps happening, the fix usually sits in server settings, plugins, code or the database.
500 server errors are fixable whether they are at visitor level or in the server settings. In this guide, you will learn:
In simple words, the server knows it failed. It does not know how to describe the failure clearly for the browser.
Therefore, you find 500 error codes look different from site to site. Some websites show a plain white page with text like:
Now that the meaning is clearer, the next step is to understand what usually triggers a 500 error.
Given below are the most common causes:
This is why the very first step is always to reload the page and try basic browser fixes.
If permissions are wrong, it may show errors. The server might not be able to access critical files needed to load the page. This can show a 500 error code.
A commonly recommended standard is:
Common .htaccess issues include:
For WordPress, database connection issues can appear when the credentials are wrong. This often happens inside a configuration file like wp-config.php.
If a site tries to load or process a very large file, it may fail and show a 500 server error. That’s why websites often use lazy loading to delay heavy images and media until they are needed.
This is why, if all fixes fail, contacting the hosting provider is usually the final step for you.
Following is the table to help you understand the 5XX error family.
An HTTP 500 Server Error is a server side error. It affects user experience and business performance. This happens because the page fails to load properly.
Did you know that 41% of the companies report their hourly downtime cost between $1 million and $5 million in 2025?
A 500 error means the server hit a problem and could not complete the request. First, reload the page and clear cache. This helps rule out local glitches. If it keeps happening, the fix usually sits in server settings, plugins, code or the database.
500 server errors are fixable whether they are at visitor level or in the server settings. In this guide, you will learn:
- What is 500 internal server error
- Why an HTTP 500 error happens
- How an HTTP 500 error can look on different sites
- How to fix HTTP 500 errors step by step
- Does HTTP 500 errors affect SEO
- How to prevent 500 errors
- How to reduce the chances of the error coming back
What Is 500 Internal Server Error
The HTTP 500 Internal Server Error is a generic status code. It appears when the server hits an unexpected problem and cannot provide a clear message.In simple words, the server knows it failed. It does not know how to describe the failure clearly for the browser.
Therefore, you find 500 error codes look different from site to site. Some websites show a plain white page with text like:
- 500 Internal Server Error
- HTTP Error 500
- HTTP Status 500 – Internal Server Error
- Internal Server Error 500
- 500. That’s an error
Now that the meaning is clearer, the next step is to understand what usually triggers a 500 error.
Why Do HTTP 500 Server Error Happens
A 500 error is a general server side failure. The cause is usually one of these areas: configuration, code, database, server resources or third party components. It can be caused by:- Server settings
- Broken website files
- Database issues
- Plugin conflicts
Given below are the most common causes:
1. Temporary Connectivity Issues and Browser Cache Problems
Sometimes the website is fine. A visitor browser may hold corrupted cache files or broken cookies. This can cause loading problems or show a 500 server error even when the website is fine.This is why the very first step is always to reload the page and try basic browser fixes.
2. Incorrect File and Folder Permissions
Websites run on servers with strict permission rules. These permissions decide whether a file can be read, written or executed.If permissions are wrong, it may show errors. The server might not be able to access critical files needed to load the page. This can show a 500 error code.
A commonly recommended standard is:
- Files: 644
- Folders: 755
3. Problems with the .htaccess File
The .htaccess file is a configuration file used on many servers. It controls important rules like redirects, rewrite rules and security settings for you. But a small mistake in this file can crash the website.Common .htaccess issues include:
- Syntax errors
- File corruption
- Wrong root folder path in rewrite rules
- RewriteBase pointing to a folder that does not exist
4. Plugin and Theme Conflicts
If a website is built on WordPress, a 500 server error often happens after:- Installing a new plugin
- Updating a plugin
- Updating a theme
- Switching or editing a theme
- A plugin that changes rewrite rules or server behaviour
5. Wrong PHP Version
Many websites rely on PHP. If the PHP version is incompatible with a plugin, theme or site code, scripts may fail and produce 500 server errors.6. PHP Memory Limit Issues
Another common issue is memory limit. If a site exceeds its allowed PHP memory limit, scripts can crash. The server then returns a 500 error code because it cannot complete the request.7. Database Errors and MySQL Server Problems
Most modern websites use a database to store content and settings. The site may produce 500 server errors if the database is corrupted. It can also happen if the site cannot connect to the database.For WordPress, database connection issues can appear when the credentials are wrong. This often happens inside a configuration file like wp-config.php.
8. Large Files on the Website
In some hosting environments, very large files can cause issues for you. For example, log files can become huge over time and cause access problems. Some shared hosting setups also have file size limits for what can be served through the web.If a site tries to load or process a very large file, it may fail and show a 500 server error. That’s why websites often use lazy loading to delay heavy images and media until they are needed.
9. Server Overload or Hosting Problems
Sometimes the website configuration is fine, but the server is not. It may be overloaded, under maintenance or having a service crash. In these cases, the 500 server error is a sign of a hosting side issue. It does not necessarily mean you changed something on the website.This is why, if all fixes fail, contacting the hosting provider is usually the final step for you.
Common HTTP 5XX Server Error Codes and Their Meanings
To understand the 500 server error, it is important to understand the wider 5XX family. These codes often appear together during server failures.Following is the table to help you understand the 5XX error family.

Understanding these distinctions helps you identify whether an issue is:
Google confirms that frequent HTTP 500 errors affect the page rankings. It stops Googlebot from crawling the pages and the pages can even be removed from the search results.
- Configuration related
- Resource based
- Caused by upstream dependencies
Common Causes of 500 Server Error
Although the 500 error code itself is vague, you can usually trace the underlying causes. Most of them fall into a few well defined categories. These are discussed below:1. Server Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations are among the most frequent issues. These include:- Incorrect directives in configuration files such as .htaccess
- Wrong file or folder permissions preventing access
- Invalid rewrite rules or root directory paths
Google confirms that frequent HTTP 500 errors affect the page rankings. It stops Googlebot from crawling the pages and the pages can even be removed from the search results.
2. Programming Errors
The website servers rely on codes written in languages such as PHP, Python or Ruby. A 500 error may occur due to a number of reasons. They may include:- Syntax errors
- Unhandled exceptions
- Deprecated or incompatible functions
- Runtime errors
3. Database Issues
Modern websites depend heavily on databases. Some of the common database related issues that results in 500 internal server errors include:- Failed database connections
- Corrupted tables
- Incorrect credentials
- Long running queries
- Timed out queries
4. Insufficient Server Resources
Another cause of the HTTP 500 error is that servers have limits. A 500 error may appear when:- Memory limits are exceeded
- CPU usage spikes during high traffic
- Disk space runs out
- Too many concurrent processes are running
5. Faulty Third Party Integrations
Some of the causes of 500 server errors are plugins, themes, extensions and external APIs. Common issues include:- Outdated plugins or themes
- Incompatible updates
- External API failures
- Conflicts between third party components
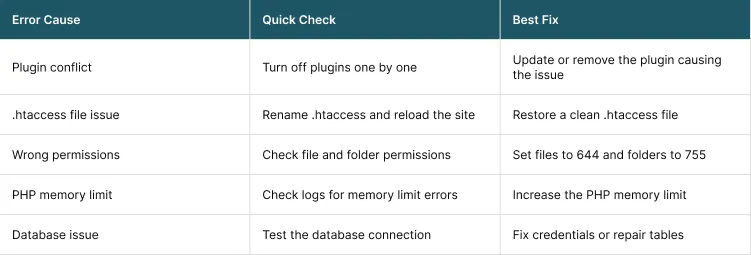
How to Troubleshoot 500 Server Error
Troubleshooting steps for 500 errors can be explained at two levels. These are;- Troubleshooting Steps for Users
- Troubleshooting Steps for Administrators
How to Troubleshoot 500 Server Error at User Level
To troubleshoot the 500 errors at user level, visitors have limited control. Given below are a few steps that can help you rule out your issues:1. Refresh the page
Refresh the page. It helps you resolve the temporary glitches or brief server hiccups.2. Clear browser cache and cookies
Corrupted cached data can interfere with requests. So, you can also try clearing browser cache and cookies.3. Try a different browser or device
You can always try a different browser or a device. This helps determine whether the issue is browser specific.4. Try again later
500 error is a server side problem. So, waiting is often the only option while administrators resolve the issue. If you find the error across devices and networks, the issue is almost certainly on the website’s server.How to Troubleshooting 500 Internal Server at Administrator Level
To troubleshoot the 500 errors at admin level, website owners must take a deeper and more structured approach. Following are the steps that can help:1. Inspect Server and Application Logs
Server logs and application logs (such as PHP error logs) usually show the exact failure point. They often contain:- Exact error messages
- File paths
- Stack traces
- Timestamps
- Configuration based
- Code related
- Resource driven
2. Check the .htaccess File
The .htaccess file is a frequent cause of 500 errors. To diagnose it, you should:- Inspect it for syntax errors
- Check rewrite rules and root paths
- Temporarily rename the file to see if the site loads
3. Deactivate Plugins and Themes
To troubleshoot 500 errors for CMS platforms like WordPress, you should try:- Disabling all plugins
- Reloading the website
- Reactivating plugins one by one to find the faulty component
- Switching to a default theme to rule out theme related errors
4. Increase PHP Memory Limits
You can also try increasing PHP memory limits. If logs indicate memory exhaustion, increasing the PHP memory limit can resolve your issue instantly.Resource heavy sites often require higher limits than default configurations allow.
5. Verify File and Folder Permissions
Verifying file and folder permission may help you fix the 500 errors. Ensure permissions follow recommended standards:- Files: 644
- Folders: 755
6. Contact the Hosting Provider
If none of the above steps work for you, the problem may be server level. Hosting providers can:- Check server health
- Review system level logs
- Identify overloads or outages
- Restart affected services
Does 500 Server Error Affects SEO and Performance
Yes, HTTP 500 errors affect SEO and performance of the page.From a user experience perspective, repeated server errors reduce trust and increase bounce rates. Users rarely return to sites that appear unreliable.
From an SEO perspective, prolonged or frequent 5XX errors can affect your business negatively. It can impact your performance in the following way:
- It prevents pages from being crawled
- It removes URLs from search engine indexes
- It lowers overall site rankings
- It signals poor server reliability to search engines
If you want to learn more about SEO and its impact, read our blog on SEO checklist for 2026.
How to Prevention 500 Server Error
Long term stability of the website needs you to be proactive. Proactive maintenance rather than reactive helps you prevent HTTP 500 errors.Key practices to prevent the HTTP internal server errors include:
- Regularly updating server software, plugins and themes
- Testing changes in a staging environment before deployment
- Monitoring server resources and uptime
- Scheduling frequent backups
- Optimising database queries and server configuration
- Removing unused plugins and extensions
Conclusion
HTTP 500 server error tells you that there is a problem in the server environment. It is generic which is why most of the time you will be frustrated. But the good thing is, it is always manageable when you approach it systematically.You can easily resolve these HTTP 500 server errors by:
- Understanding the full range of 5XX server error codes
- Recognising common causes
- Following structured troubleshooting steps
- Investing in preventive maintenance
Seeing HTTP 500 errors and not sure why your site keeps breaking?
Server errors can hurt traffic and rankings if ignored. Contact us to find the cause, fix the issue and keep your website stable and search engine friendly.
Faqs
HTTP 500 means the server hit an unexpected problem and could not complete a valid request. It is a general error, so it does not tell the exact cause.
- 500 means the server failed but cannot explain the exact reason.
- 502 means the server got a bad response from another server it depends on.
- 503 means the server is temporarily unavailable due to overload or maintenance.
5XX codes mean the problem is on the server side. The server could not complete the request, even though the request was valid.
Step 1: Check the API/server error logs to find the real error message.
Step 2: Confirm database credentials are correct (username, password, host, database name).
Step 3: Check if the database server is running and responding.
Step 4: Test network access between the API server and the database.
Step 5: Check database connection limits (too many open connections can crash requests).
Step 6: Review the code to close unused connections and handle errors properly.
Step 7: Confirm the correct database driver is installed and configured.
Step 2: Confirm database credentials are correct (username, password, host, database name).
Step 3: Check if the database server is running and responding.
Step 4: Test network access between the API server and the database.
Step 5: Check database connection limits (too many open connections can crash requests).
Step 6: Review the code to close unused connections and handle errors properly.
Step 7: Confirm the correct database driver is installed and configured.
Step 1: Open server logs and database logs and find the exact connection failure line.
Step 2: Re-check database settings in your config file (one wrong character can break it).
Step 3: Confirm the database server is online (restart service if needed).
Step 4: Test connection manually from the same server (to confirm it is reachable).
Step 5: Check if the database has hit max connections or timeouts.
Step 6: Fix the app code so it uses connection pooling or closes connections after use.
Step 7: Confirm drivers, SSL settings, and ports match your database setup.
Step 2: Re-check database settings in your config file (one wrong character can break it).
Step 3: Confirm the database server is online (restart service if needed).
Step 4: Test connection manually from the same server (to confirm it is reachable).
Step 5: Check if the database has hit max connections or timeouts.
Step 6: Fix the app code so it uses connection pooling or closes connections after use.
Step 7: Confirm drivers, SSL settings, and ports match your database setup.
Yes, sometimes. Clearing browser cache can help visitors because the browser may be loading an old broken version of the page. After clearing cache, reload the page.
Step 1: Refresh the page and confirm the URL is correct.
Step 2: Check internet connection and try a different network if possible.
Step 3: Restart Chrome and update it to the latest version.
Step 4: Open the site in Incognito mode to rule out extensions and cache issues.
Step 5: Clear browsing data (cache and cookies) and try again.
Step 6: Run a quick malware scan and remove suspicious extensions. Step 7: Free up device storage and memory, then restart the device.
Step 8: If nothing works, uninstall and reinstall Chrome.
Step 2: Check internet connection and try a different network if possible.
Step 3: Restart Chrome and update it to the latest version.
Step 4: Open the site in Incognito mode to rule out extensions and cache issues.
Step 5: Clear browsing data (cache and cookies) and try again.
Step 6: Run a quick malware scan and remove suspicious extensions. Step 7: Free up device storage and memory, then restart the device.
Step 8: If nothing works, uninstall and reinstall Chrome.
502 Bad Gateway is used when a server is acting as a gateway or proxy and receives an invalid response from an upstream server. It usually means the website’s server is not getting a proper reply from another server it relies on.
A 500 error can be triggered by server side problems like:
- wrong server configuration (often .htaccess issues)
- out of memory or high CPU load
- broken code or unhandled errors
- wrong file and folder permissions
- database connection failures or timeouts
- plugin or theme conflicts (very common in WordPress)
500 errors are server-side errors that appear when a website server runs into an unexpected problem and cannot complete a valid request. They do not point to one clear issue. Instead, they act as a general warning that something on the server side is broken, such as configuration settings, code, database connections, or server resources.

